What is an autonomous car?
An autonomous car, also known as a self-driving car, is a vehicle that can operate without human input. Unlike traditional cars, which require a human driver to operate them, autonomous cars use a combination of sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence (AI) to navigate roads and make decisions.
How big is the Autonomous car market?
In 2020, the worldwide market for autonomous vehicles was estimated to be worth $76,126.43 million, and it is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 40.1% between 2021 and 2030, eventually reaching a total value of $2,161,787.29 million by 2030.
What are the top companies involved in Autonomous driving cars?
Tesla: Tesla has been developing and testing autonomous driving technology for several years and is known for their Autopilot system, which offers semi-autonomous driving capabilities to Tesla owners.
Waymo: Waymo, a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc., is considered to be a leader in the autonomous driving industry. They have been testing their self-driving technology on public roads since 2009 and have accumulated more than 20 million miles of autonomous driving.
General Motors: General Motors has been working on autonomous driving technology through their Cruise Automation subsidiary, with plans to launch a ride-sharing service using autonomous vehicles.
Uber: Uber has been testing autonomous driving technology in a number of cities, with the goal of eventually offering a self-driving ride-sharing service.
Baidu: Baidu, a Chinese technology company, has been developing autonomous driving technology and has partnerships with several major automakers.
It’s worth noting that the autonomous driving industry is constantly evolving, and the leading companies in the field may change over time.
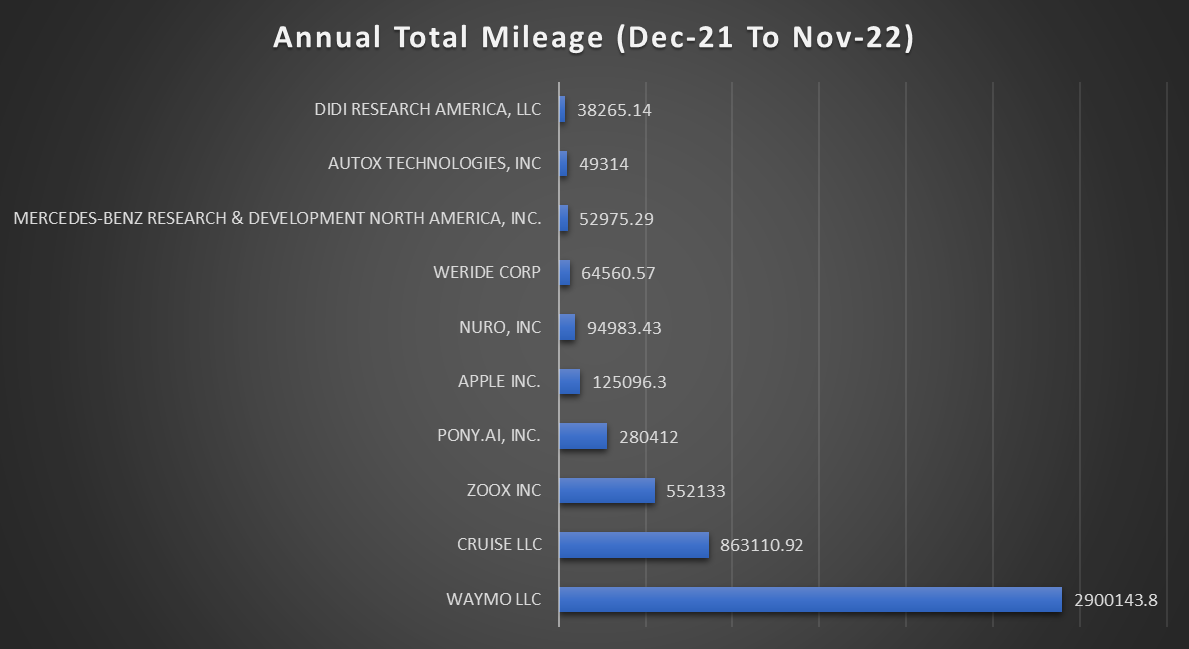
Below chart shows the annual total mileage driven by the autonomous cars from Dec-21 to Nov-22.
For more details, please check https://www.dmv.ca.gov/ official website.
What are the levels of Autonomous Cars?
Autonomous cars can be classified into different levels of autonomy, ranging from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (full automation). At Level 0, the car is fully manual and requires a human driver to control it. At Level 5, the car is fully autonomous and can operate without any human input.

Below are the levels of autonomous cars as we know:
Level 0: No Automation – The car is fully manual and requires a human driver to control it.
Level 1: Driver Assistance – The car has some basic driver assistance features, such as cruise control or automatic braking, but still requires a human driver to control the vehicle.
Level 2: Partial Automation – The car has some advanced driver assistance features, such as lane-keeping assist and adaptive cruise control, and can operate in some situations without human input, but still requires a human driver to remain attentive and ready to take control at any time.
Level 3: Conditional Automation – The car can operate autonomously in some situations, such as on highways, but still requires a human driver to be present and ready to take control if necessary.
Level 4: High Automation – The car can operate autonomously in most situations and environments, but still has some limitations, such as requiring human input in extreme weather conditions.
Level 5: Full Automation – The car is fully autonomous and can operate without any human input in all situations and environments.
How autonomous car works or operated?
Autonomous cars operate using a combination of sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to perceive their environment, analyze data, and make decisions about how to navigate and drive on the road.
Here’s a general overview of how an autonomous car works:
Perception: Autonomous cars use a range of sensors, such as radar, lidar, and cameras, to perceive their environment. These sensors detect obstacles, road markings, and other vehicles and objects in the car’s surroundings.
Localization: Autonomous cars use GPS and other technologies to determine their location and position on a map.
Mapping: Autonomous cars use detailed maps to understand their surroundings and plan their route. The car’s sensors and GPS information are used to match the car’s position on the map.
Decision-making: Autonomous cars use AI algorithms to analyze sensor data and make driving decisions based on machine learning and rule-based decision-making. This enables the car to navigate the road, change lanes, and stop at traffic lights.
Actuation: Once a decision has been made, the car’s actuators control the car’s acceleration, braking, and steering to execute the decision.
Monitoring: Throughout the entire driving process, autonomous cars continuously monitor their environment and performance to ensure safe and reliable driving.
Overall, autonomous cars are potentially safer, efficient, and convenient due to their technology that enables operation without human input. However, the development of autonomous cars also brings ethical, regulatory, and social challenges. Let’s discuss them below.
Here are some of the main challenges faced by autonomous cars:
Safety: One of the biggest challenges is ensuring the safety of autonomous cars, both for the passengers and for other road users.
Legal and regulatory issues: There are a number of legal and regulatory issues surrounding the use of autonomous cars, including liability in the event of an accident, data privacy, and cybersecurity.
Ethical issues: Autonomous cars raise ethical concerns regarding programming decisions during difficult situations, like hitting a pedestrian or another car.
Public acceptance: There may be resistance from some people to using autonomous cars, particularly those who are used to driving themselves.
Technical challenges: Developing reliable sensors and software, and ensuring operation in different conditions are key challenges for autonomous cars.
Infrastructure: The widespread adoption of autonomous cars may require significant changes to road infrastructure, such as adding dedicated lanes or modifying traffic signals to accommodate autonomous vehicles.
Cybersecurity: Autonomous cars are vulnerable to cyberattacks, which could potentially result in the loss of control of the vehicle or the theft of personal information.
Overall, addressing these challenges will be critical to the successful development and deployment of autonomous cars. We can see the benefits of autonomous cars below.
Here are some of the main benefits of autonomous cars:
Improved safety: Autonomous cars can reduce accidents caused by human error, like speeding, distracted driving, and drunk driving.
Increased mobility: Autonomous cars can improve accessibility for elderly or disabled individuals who are unable to drive.
Reduced traffic congestion: Autonomous cars could reduce traffic congestion by optimizing traffic flow and reducing the need for parking.
Improved fuel efficiency: Autonomous cars could be programmed to drive in a more fuel-efficient manner, reducing fuel consumption and emissions.
Increased productivity: Autonomous cars could allow passengers to work or relax during their commute, increasing productivity and reducing stress.
Cost savings: Autonomous cars may decrease costs associated with car ownership, insurance, and maintenance.
Improved urban planning: Autonomous cars may enhance urban planning by reducing parking needs and allowing for more efficient space utilization.
Autonomous cars have significant potential to revolutionize transportation, offering various benefits. However, addressing challenges and risks is crucial for realizing the full potential benefits of autonomous cars. This has been discussed in the above section already.

Overall, autonomous cars offer potential benefits such as increased safety, reduced traffic congestion, and improved mobility. However, challenges such as regulatory issues, cybersecurity concerns, and ethical dilemmas must be addressed. With continued development and testing, autonomous cars have the potential to transform transportation and improve quality of life.
Check out my latest posts in my blog and please share your feedback or suggestions.




Pingback: Hydrogen car vs Electric car - Which is better? | The Daily Access