J. Robert Oppenheimer was a famous Physicist and one of the major contributors in the development of atomic bomb. He was born in New York City in 1904, his role in the World War II was very critical and in development of nuclear weapon. In the below article, let’s see the life of J. Robert Oppenheimer and his role in the Manhattan Project including his impact on modern physics.
Education and Career

Oppenheimer enrolled at Harvard University in 1921 to study physics and chemistry. In 1927, he graduated with a doctorate in physics from the University of Göttingen in Germany. His examiners complimented his quantum mechanics thesis as one of the greatest they had ever read.
Oppenheimer spent two years pursuing research in Europe after earning his Ph.D. before coming home to take a job as a professor at the University of California, Berkeley.
What is the Manhattan Project?
The Manhattan Project was a top-secret research and development program led by the United States during World War II to produce the first nuclear weapons. Oppenheimer was appointed as the scientific director of the project. He played a key role in the research and development of the atomic bomb, which was later used by the United States to end the war against Japan.

The project involved large number of scientists and engineers to work at many locations in the United States. A German researcher named Otto Hahn realized that nuclear fission can be used to create atomic bombs, later the project received huge funding from the U.S. government. This allowed the project to acquire more resources that are required to develop nuclear weapons.
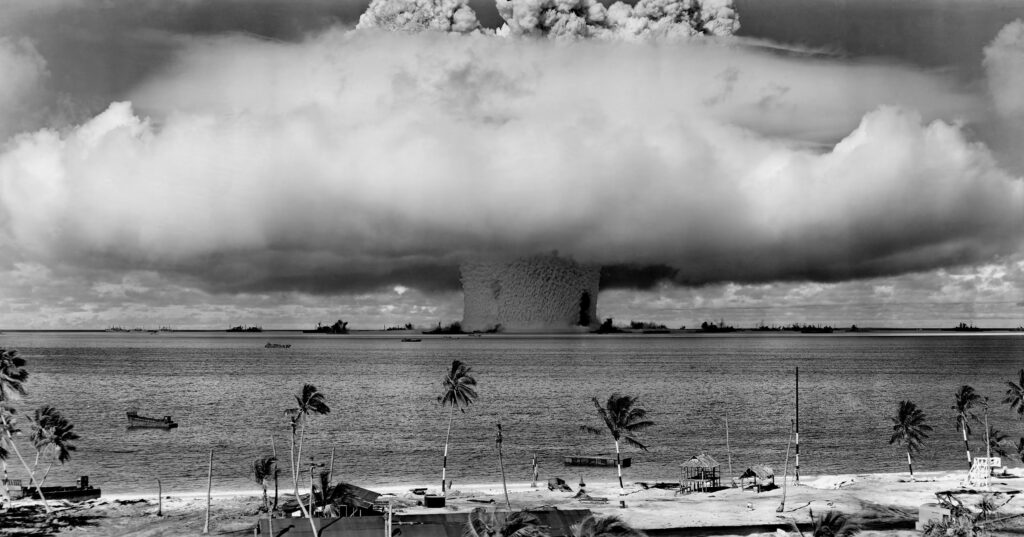
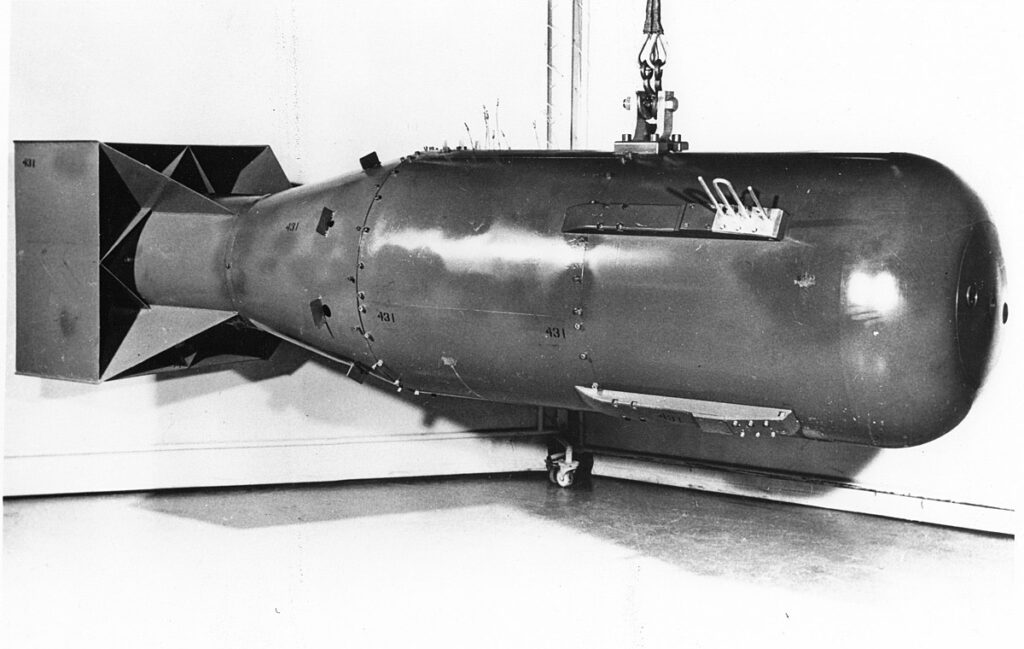
Little Boy and Fat Man – Bombs that destroyed Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945
Oppenheimer’s team developed two atomic bombs: The Little Boy, which was dropped on Hiroshima on August 6, 1945, and the Fat Man, which was detonated on Nagasaki on August 9, 1945. These attacks, which resulted in the deaths of roughly 200,000 people, the bulk of whom were civilians, utterly destroyed the two cities.
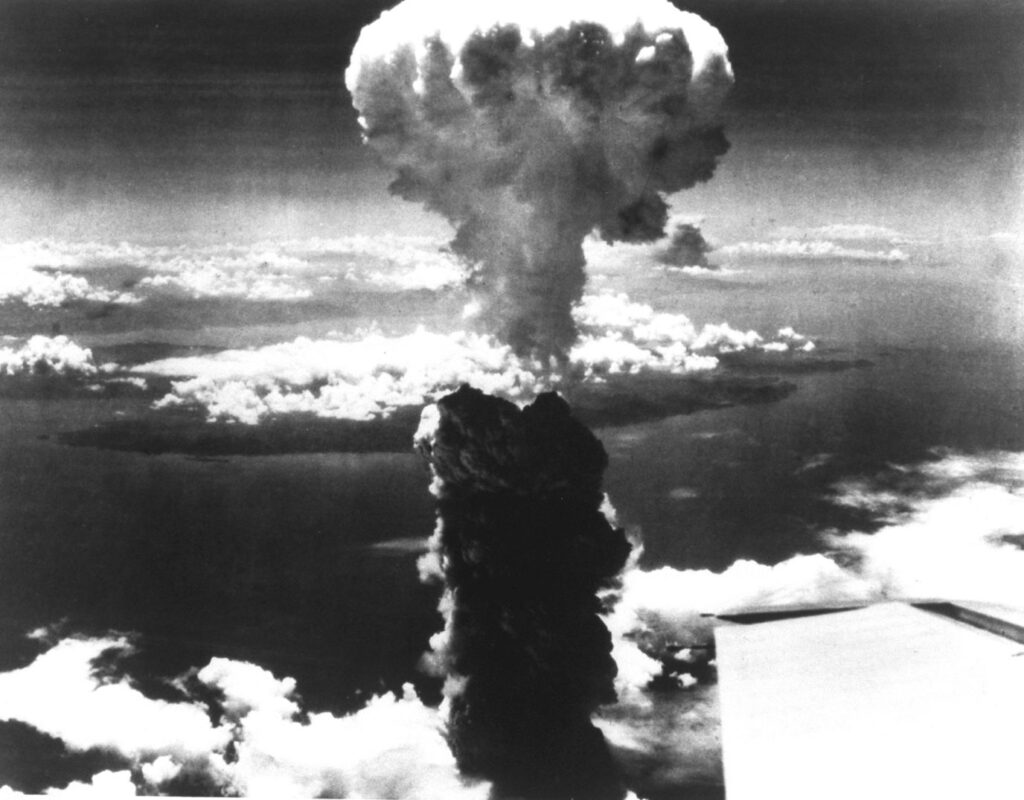

Although the Manhattan Project was a momentous milestone in science and technological history, it also aroused moral concerns about the deployment of nuclear weapons. The project’s primary contributor, Oppenheimer, came out strongly against the nuclear arms race and their use in general. In 1954, he lost his post as a government counsellor and had his security clearance revoked because of his opposition to the development of the hydrogen bomb. Oppenheimer’s reputation as a bright physicist and pioneer in the scientific community endures despite this.
Blast Radius of Little Boy and Fat Man Atomic Bomb
The Little Boy bomb’s blast radius was roughly 1.6 miles (2.6 km), and the city of Hiroshima sustained significant destruction as a result. The energy produced by the explosion was massive, roughly equal to 15,000 Tonnes of TNT.
The blast radius of the Fat Man atomic bomb was approximately 1.5 miles or 2.4 kilometers. However, the radius of total destruction caused by the bomb was larger, extending up to 2.5 miles or 4 kilometers due to the resulting fires.
Little Boy or Fat Man, which was more destructive?
Physically, the “Fat Man” bomb was bigger than the “Little Boy” bomb. “Little Boy” was a uranium gun-type bomb, whereas “Fat Man” was a plutonium implosion-type bomb. The two bombs’ destructive potential, however, was not inversely correlated with their size. “Fat Man” was more powerful than “Little Boy”, with an explosive yield of about 21 kilotons of TNT compared to “Little Boy’s” yield of around 15 kilotons
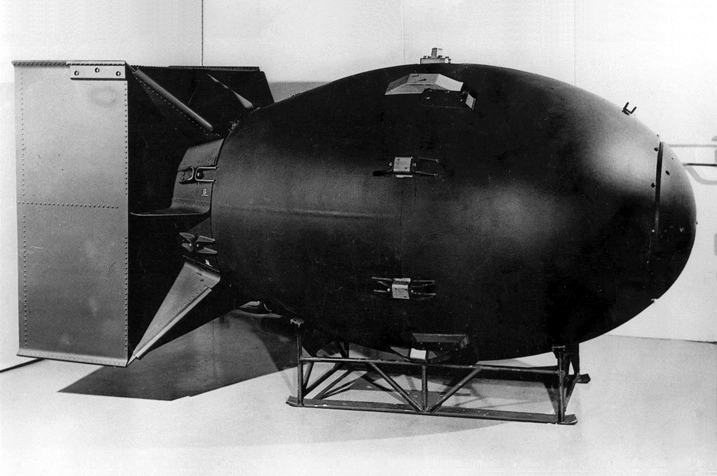

According to estimates, 200,000 people died as a result of the two atomic bombings combined, though the precise figure is difficult to ascertain due to the long-term consequences of radiation exposure.
Oppenheimer’s Political View
While Oppenheimer was revered for his scientific contributions to the United States, his political views also made him a contentious figure. Oppenheimer was openly left-leaning, which attracted the attention of the US government during the Cold War’s height. He was charged with espionage and sympathies for the Communist Party. Oppenheimer’s federal career was effectively ended when his security clearance was revoked as a result in 1954.
View on Oppenheimer
It is impossible to overstate Oppenheimer’s contributions to science and the creation of the atomic bomb. His management of the Manhattan Project had a crucial role in the successful construction of the bomb, and his contributions to the fields of astrophysics and quantum mechanics have had an ongoing impact on scientific understanding and study.
There has been numerous books, films and documentaries about Oppenheimer’s life and work which explores the complex legacy of the scientist who played a pivotal role in the creation of one of the most destructive weapons in human history.
Although the creation of the atomic bomb remains a dark chapter in human history, Oppenheimer’s contributions to science and his standing as a visionary leader and physicist will be studied and celebrated for years to come.




