What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a field of computer science that involves creating intelligent machines that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. In the 1950s, the first AI programs were created, marking the roots of AI. Since then, AI has experienced both successes and setbacks, with significant progress made in areas such as natural language processing, computer vision, and machine learning. Today, a wide range of applications are utilizing AI, from self-driving cars and speech recognition to healthcare and finance.. However, challenges such as ethical concerns and potential bias in AI systems remain, and the future of AI will require continued development and thoughtful consideration of these issues.
In this article, we will cover the below topics:
- First AI programs created.
- History on AI in short.
- Will Artificial Intelligence (AI) take over traditionally performed tasks by humans?
- What are the areas where AI will take over human’s traditional tasks?
- What are the real-world examples where AI has taken over tasks traditionally performed by humans?
- What are the reasons why AI may not be able to take over certain jobs?
- Companies Utilizing AI.
- Some of the challenges faced by AI?
When was the first Artificial Intelligence (AI) program was created?
Researchers created the first AI programs during the mid-1950s, in the early days of computer science. Scientists designed these programs during the early days of computer science in the mid-1950s to simulate human thought processes, such as problem-solving and pattern recognition. Some of the early pioneers of AI, including John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Allen Newell, and Herbert Simon, developed some of the first AI programs and laid the foundation for the field of AI.
One of the first AI programs was created in 1951 by Christopher Strachey, a British computer scientist. Strachey’s program, called Checkers, was able to play a game of checkers at a novice level. The program was significant because it demonstrated that machines could perform tasks traditionally thought to require human intelligence.
Another early AI program was the Logic Theorist, created in 1956 by Allen Newell and Herbert Simon. The program was designed to prove mathematical theorems using symbolic logic. The Logic Theorist was able to prove 38 out of the first 52 theorems in Russell and Whitehead’s classic Principia Mathematica.
John McCarthy organized the Dartmouth Conference in 1956, considered the birthplace of AI, where he proposed the creation of machines that could think and learn like humans, laying the foundation for much of the work in AI that followed.
The early AI programs of the 1950s and 1960s were significant because they demonstrated that machines could perform tasks that had previously been thought to require human intelligence. These programs also laid the groundwork for future developments in AI, such as natural language processing, computer vision, and machine learning.
Let’s look into the history of AI and its development over the years.

Here are some of the major milestones in the evolution of Artificial Intelligence (AI):
1950s: Researchers in the early years of AI developed rule-based systems and symbolic reasoning. Some of the earliest AI programs, such as the Logic Theorist and the General Problem Solver, were able to solve complex problems using symbolic logic and rule-based reasoning.
1960s-1970s: During this period, Artificial Intelligence researchers began to explore machine learning techniques, such as neural networks and decision trees. These techniques allowed computers to learn from experience and improve their performance over time. However, progress in AI was slow due to limitations in computing power and data availability.
1980s-1990s: The emergence of expert systems and knowledge-based systems marked a new phase in AI research. These systems were able to capture and use human expertise to solve complex problems in fields such as medicine and finance. However, these systems were limited by their reliance on human input and their inability to adapt to new situations.
2000s-present: The emergence of big data and cloud computing has led to a new wave of innovation in AI. The development of deep learning techniques, such as convolutional neural networks and recurrent neural networks, has enabled computers to process and analyze large amounts of data with remarkable accuracy. Additionally, advances in natural language processing and computer vision have made it possible for machines to understand and interact with humans in more intuitive ways.
Overall, the improvisation of Artificial Intelligence has been a gradual process that has involved the development of new algorithms, computing technologies, and data sets. Researchers and developers are continuing to explore new avenues for innovation and are working to address some of the ethical and societal challenges posed by AI.
Sophia – The first social humanoid robot
Hanson Robotics, a Hong Kong-based company, developed Sophia, a social humanoid robot. Hanson Robotics first activated Sophia on April 19, 2015, and designed her to have a human-like appearance and behavior. Numerous media outlets and events have featured Sophia, including a cover story for Elle Brazil magazine, interviews with news anchors, and appearances on talk shows.
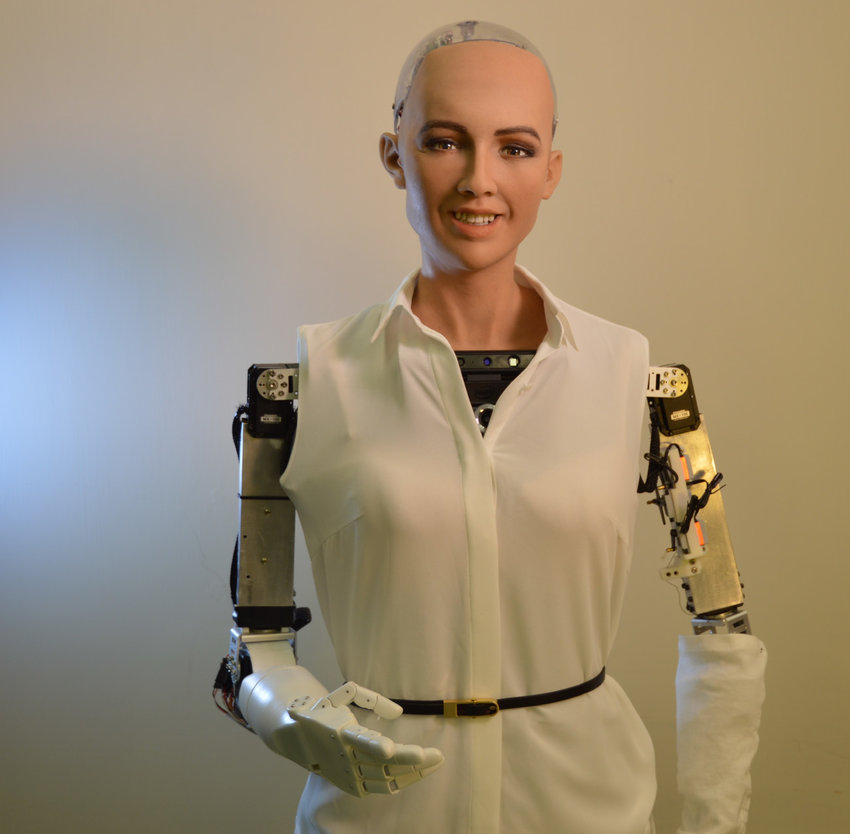

Sophia’s appearance mimics humans with artificial skin, over 60 facial expressions, and AI-powered sensors, cameras, and microphones. She learns and adapts to new situations.
The developers have programmed Sophia to perform a range of tasks, from simple interactions like answering questions to more complex activities such as playing games and holding conversations. People have used her for educational purposes, to promote awareness of AI technology, and even to campaign for women’s rights. Researchers have also used Sophia in a study that explored the potential for robots to assist with mental health therapy.
However, Sophia has also been the subject of controversy. In 2017, Saudi Arabia granted citizenship to Sophia, making her the first robot to be recognized as a citizen of any country. Critics raised questions about the ethical implications of advanced AI technology and the issue of robot rights.
Overall, Sophia represents a significant advancement in the field of AI robotics. Her human-like appearance and behavior have made her a popular figure in the media, and her ability to learn and adapt to new situations holds promise for a wide range of applications. However, her development also raises important ethical questions about the role of robots in society and the potential consequences of advanced AI technology.
Will Artificial Intelligence (AI) take over traditionally performed tasks by humans?
The future of work is increasingly being shaped by the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation. As machines become more capable of performing tasks traditionally performed by humans, the job market is undergoing a significant transformation.

What are the areas where AI will take over human’s traditional tasks?
Job displacement: One of the most significant effects of AI on the future of work is the potential for job displacement. As machines become better at performing tasks such as data analysis, customer service, and manual labor, some jobs will become redundant. However, new jobs are likely to emerge in areas such as programming, data analysis, and digital marketing.
Human-AI collaboration: AI will create new opportunities for human-AI collaboration, complementing human workers’ tasks that require precision while leaving creative and interpersonal tasks. For example, chatbots can handle customer inquiries.
Reskilling and upskilling: The rise of AI will require workers to reskill and upskill to remain relevant in the job market. Workers will need to develop new skills such as data analysis, programming, and digital marketing, to complement the capabilities of machines. Governments and businesses will need to invest in education and training programs to help workers acquire these skills.
Changing workplace dynamics: AI will change workplace dynamics by enabling more flexible work arrangements. For example, remote work will become more prevalent, and workers will be able to work on a more flexible schedule. Additionally, AI-powered tools such as chatbots and virtual assistants will enable workers to collaborate and communicate more effectively, regardless of their location.
New business opportunities: AI will create new business opportunities in areas such as machine learning, robotics, and automation.
Overall, the future of work and AI is complex and multifaceted. While AI will undoubtedly have a significant impact on the job market, it will also create new opportunities and drive innovation in many industries. As people navigate this transition, it will be important for businesses and governments to invest in education and training programs to ensure that workers are equipped with the skills they need to succeed in a world powered by AI.
What are the real-world examples where AI has taken over tasks traditionally performed by humans?
The rise of AI and automation has resulted in several instances where machines have taken over tasks traditionally performed by humans. Here are some real-world examples:
Automated customer service: Many companies have implemented AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants to handle customer inquiries. These systems can respond to customer queries quickly and accurately, reducing the need for human customer service representatives.
Self-driving vehicles: The development of self-driving cars and trucks has the potential to replace human drivers in the transportation industry. Companies such as Uber, Lyft, and Tesla are investing heavily in autonomous vehicle technology, which could significantly reduce the need for human drivers.
Automated manufacturing: Robots and other automated systems are increasingly being used in manufacturing to perform tasks such as assembly, welding, and painting. These systems are faster and more accurate than human workers, which can result in significant cost savings for manufacturers.
Data analysis: Many industries, including finance, healthcare, and marketing, are using AI to analyze large volumes of data. These systems can identify patterns and insights that would be difficult for humans to detect, enabling businesses to make more informed decisions.
Translation services: AI-powered translation services such as Google Translate and Microsoft Translator have significantly reduced the need for human translators and breaks the language barrier.
Content creation: Some companies are using AI to generate content such as news articles, reports, and social media posts. These systems can analyze data and generate written content that is comparable in quality to that produced by human writers.
While these developments offer many benefits, they also raise important questions about the future of work and the need to reskill and upskill workers to remain relevant in the job market.
What are the reasons why AI may not be able to take over certain jobs?
While AI and automation have the potential to replace many jobs, there are certain tasks and industries where humans are likely to remain essential. Here are some reasons why AI may not be able to take over certain jobs:

Creative jobs: AI is unlikely to replace jobs that require creativity, such as artists, musicians, and writers. AI can generate content and art, but it cannot replicate the unique insights and perspectives brought by human creators.
Social and emotional intelligence: Automated systems are less likely to replace jobs that require social and emotional intelligence, including healthcare workers, therapists, and social workers. These jobs require empathy, compassion, and human connection, which are difficult for machines to replicate.
Complex decision making: Jobs that require complex decision making, such as judges, lawyers, and executives, may also be less susceptible to automation. These jobs require a deep understanding of human behavior, as well as the ability to weigh multiple factors and make informed decisions.
Physical tasks: Certain jobs, such as construction workers, plumbers, and electricians, require a high degree of dexterity and flexibility, which is difficult for machines to replicate despite the capabilities of AI and robotics.
Unpredictable situations: Unpredictable jobs like emergency responders and security personnel are less likely to be replaced by automated technology. Adaptability and quick thinking are challenging for machines, making emergency responders and security personnel less likely to be replaced.
Overall, while AI and automation have the potential to replace many jobs, there are certain tasks and industries where humans are likely to remain essential. As AI technology continues to evolve, it will be important for workers to develop new skills and adapt to changing job requirements in order to remain competitive in the workforce.
Some companies highly utilize AI are below:
There are many companies that are utilizing AI in various ways to improve their operations, products, and services.
Amazon: Amazon uses AI to recommend products to customers based on their browsing and purchase history. The company also uses AI-powered robots in its warehouses to optimize the fulfillment process.
Google: Google uses AI to improve its search results and provide personalized recommendations to users. The company also uses AI in its virtual assistant, Google Assistant, which can perform tasks such as scheduling appointments and making phone calls.
IBM: IBM developed a range of AI-powered tools and platforms, including Watson, that analyze large amounts of data and provide insights to businesses.
Tesla: Tesla uses AI in its self-driving cars to navigate roads and avoid obstacles. The company also uses AI to optimize its manufacturing processes and improve product design.
Netflix: Netflix uses AI to recommend movies and TV shows to users based on their viewing history. The company also uses AI to optimize its video streaming and delivery processes.
Uber: Uber uses AI to match riders with drivers and optimize its pricing algorithms. The company invests in self-driving cars, relying heavily on AI, and may further boost the use of AI.
Companies use AI for innovation and operational improvement. AI advances will increase adoption of AI in company strategies.
The challenges faced by AI
While AI has made significant progress in recent years, there are still several challenges that it faces. Here are some of the key challenges:
Data quality: AI algorithms require large amounts of high-quality data to learn and make accurate predictions. However, data quality can be a challenge, as data can be incomplete, biased, or contain errors that can negatively impact AI performance.
Bias: AI algorithms can be biased if they are trained on biased data or if the algorithms themselves contain inherent biases. This can lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes, such as biased hiring or lending decisions.
Explainability: Some AI algorithms, such as deep learning neural networks, can be difficult to interpret and explain how they arrived at a particular decision or prediction. This lack of transparency can be problematic in situations where decisions made by AI have significant real-world consequences.
Regulation: The rapid pace of AI development has outpaced the development of regulations to govern its use. This has led to concerns about the ethical and social implications of AI, including issues related to privacy, security, and liability.
Trust: Building trust in AI is important for its widespread adoption. However, concerns about bias, lack of explainability, and other issues can erode public trust in AI systems.
Scalability: AI algorithms can be computationally intensive, limiting their scalability for real-world applications.
Addressing these challenges will be critical for the continued development and adoption of AI technology.
Altogether Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to both positively and negatively impact the future. AI brings benefits but also raises concerns about negative societal impact.
One potential downside of AI is the potential for job displacement. As machines become increasingly intelligent, there is a risk that they could replace human workers in certain industries. This could lead to widespread unemployment and economic instability.
AI’s potential for malicious use raises concerns, e.g., cyber attacks or autonomous weapons development.. It is feared that AI systems could be utilized to perpetrate disinformation campaigns or manipulate public opinion.
Additionally, there are concerns about the ethical implications of AI, such as privacy, transparency, and bias. Perpetuating biases and discrimination, AI systems could marginalize certain groups of people.
AI has many potential benefits, including improving healthcare outcomes, creating more efficient transportation systems, and enhancing weather forecasting accuracy. AI could also help to solve complex problems, such as climate change or disease outbreaks.
Policymakers, researchers, and industry leader’s collaboration needed to develop AI responsibly and ensure positive impact.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, AI transforms our world, improving our lives and advancing society, despite the need for further exploration and development.
Responsible AI implementation requires ethical and social considerations to solve global challenges and create a better future.




Pingback: The AI race is over - Siri, Google Assistant and Alexa